The individuals who appear are for illustrative purposes. All persons depicted are models and not real patients or healthcare professionals.
†Kinetic stability describes the speed of in vivo complex dissociation of gadolinium, or propensity to release Gd ions following transmetallation in vivo (in addition to thermodynamic stability).
VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) injection for intravenous use provides effective contrast enhancement at half the gadolinium dose compared to other macrocyclic GBCAs for approved indications in the U.S.1,4,5
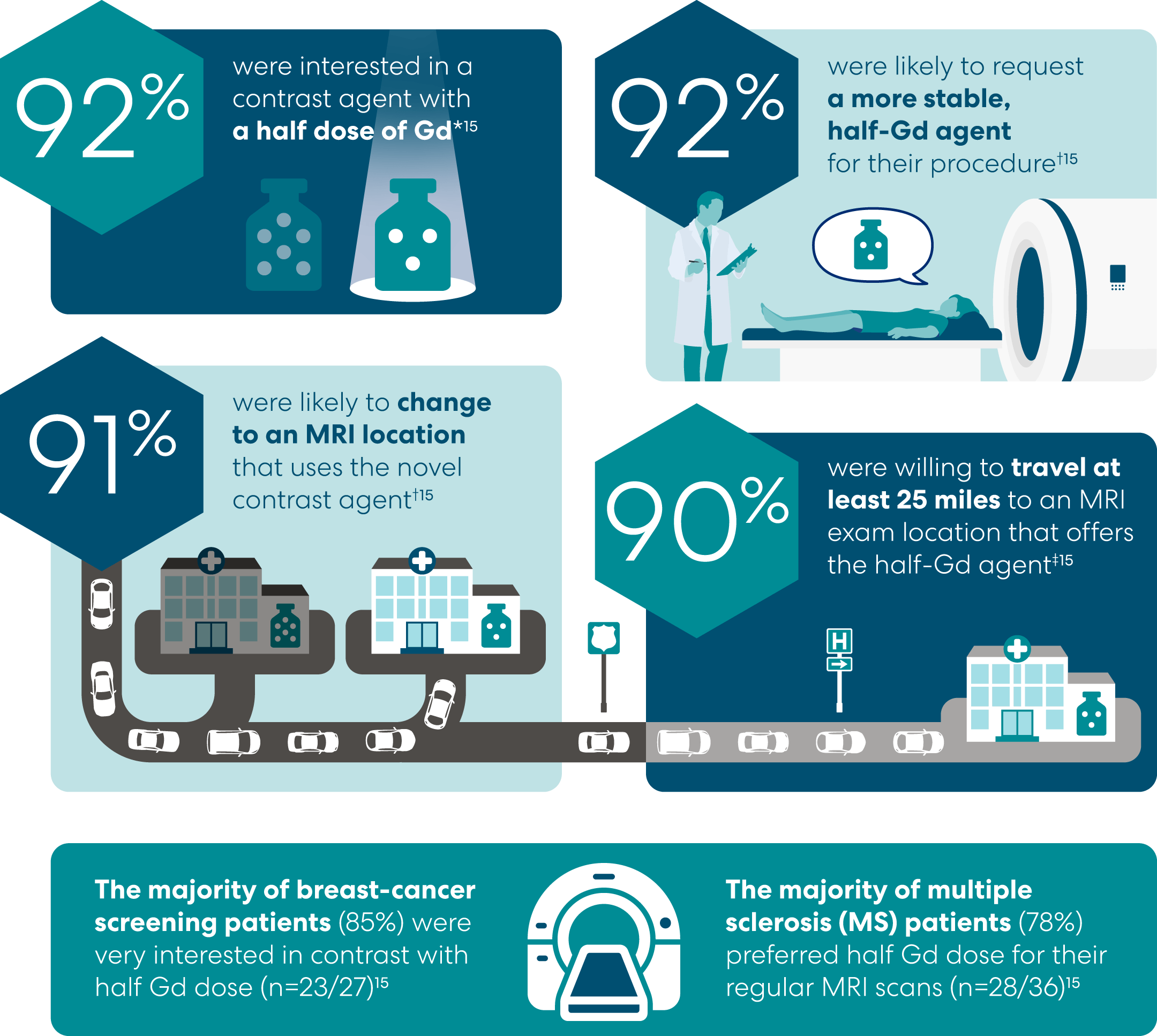
Recent Survey: MRI Patients are Interested in Their Contrast Agent
In a nationwide survey among 300 recipients of contrast MRI exams: majority of patients expressed interest in a half-Gd contrast agent*15
Patients’ Perspectives
About VUEWAY Injection
“I am a patient who would prefer to use your lower-dose contrast for my contrast MRIs. I am willing to travel to use…lower dose contrast.”
— Email correspondence from patient in Idaho receiving contrast MRI
“I require annual MRI contrast screenings…which is why I’m particularly interested in the availability of Bracco’s VUEWAY contrast agent.”
— Email correspondence from patient in Texas receiving annual contrast MRI
These are the views of two uncompensated patients, based on their individual experience, research, and/or consultation with their physician. Not all patients or physicians may have the same view or recommendations.
VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) injection for intravenous use
Three Million Doses and Counting
Bracco would like to thank professionals like you for your trust and commitment to elevating innovation in the MR suite.
Bracco & UPMC Partner on the
Latest Innovation in MR Contrast
The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center is leading the way in the use of VUEWAY injection in abbreviated breast MRI protocols, helping women with dense breast tissue feel more confident in their annual screenings and helping doctors improve the care of their patients.
Just a few of Bracco’s proud firsts
For more than 95 years, the Bracco Group has been an innovator in radiology, dedicated to developing products that help you advance the standard of care.

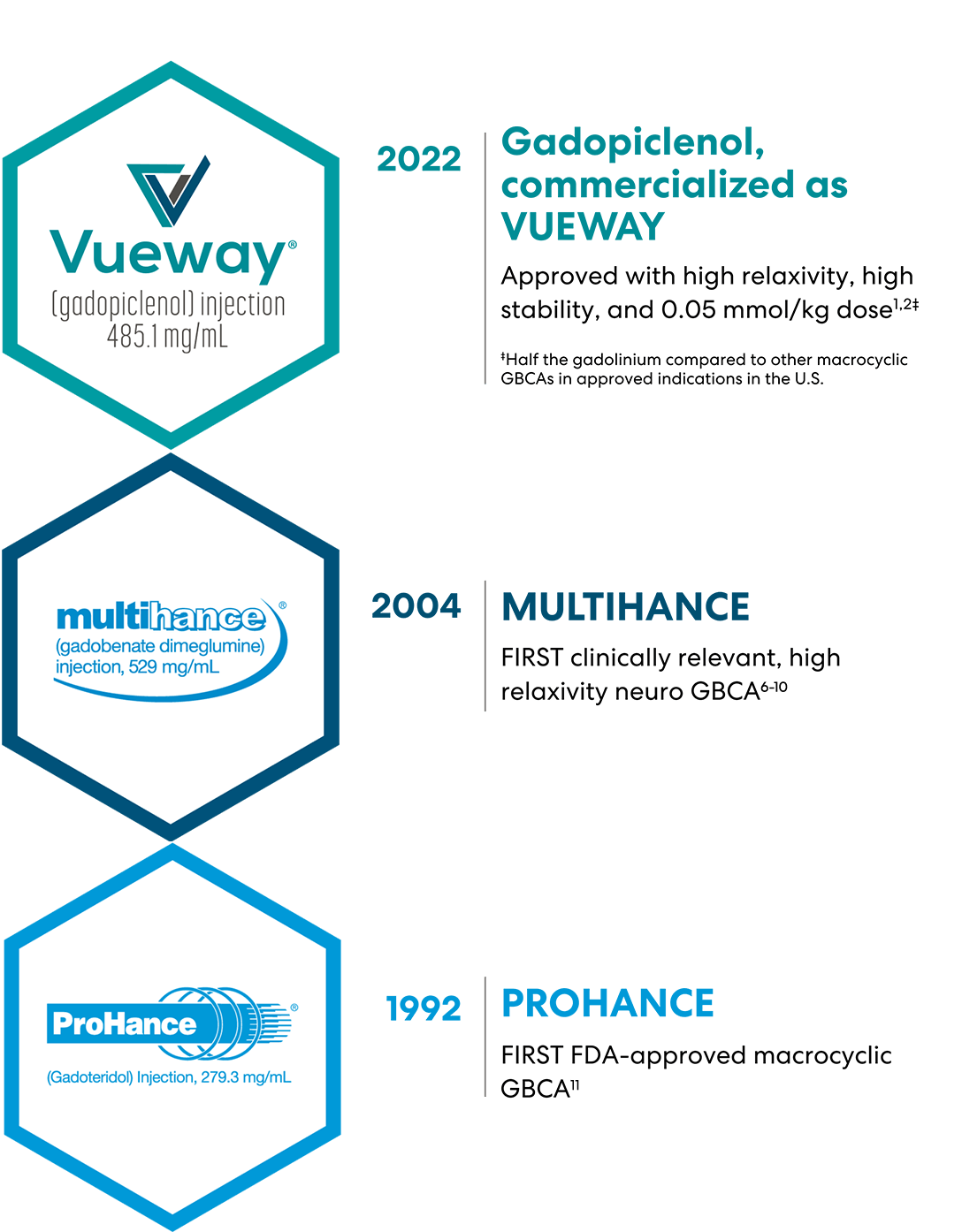
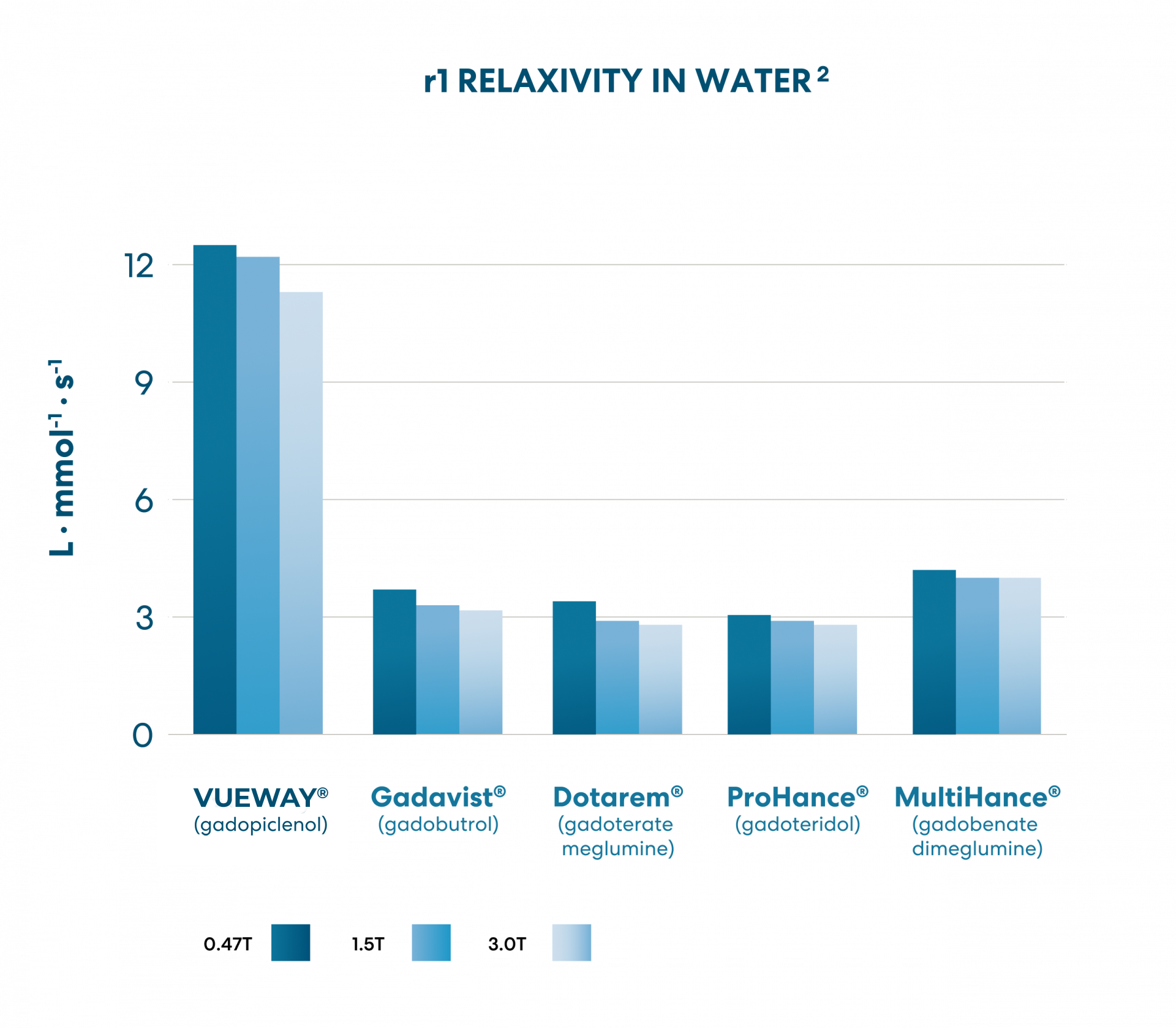
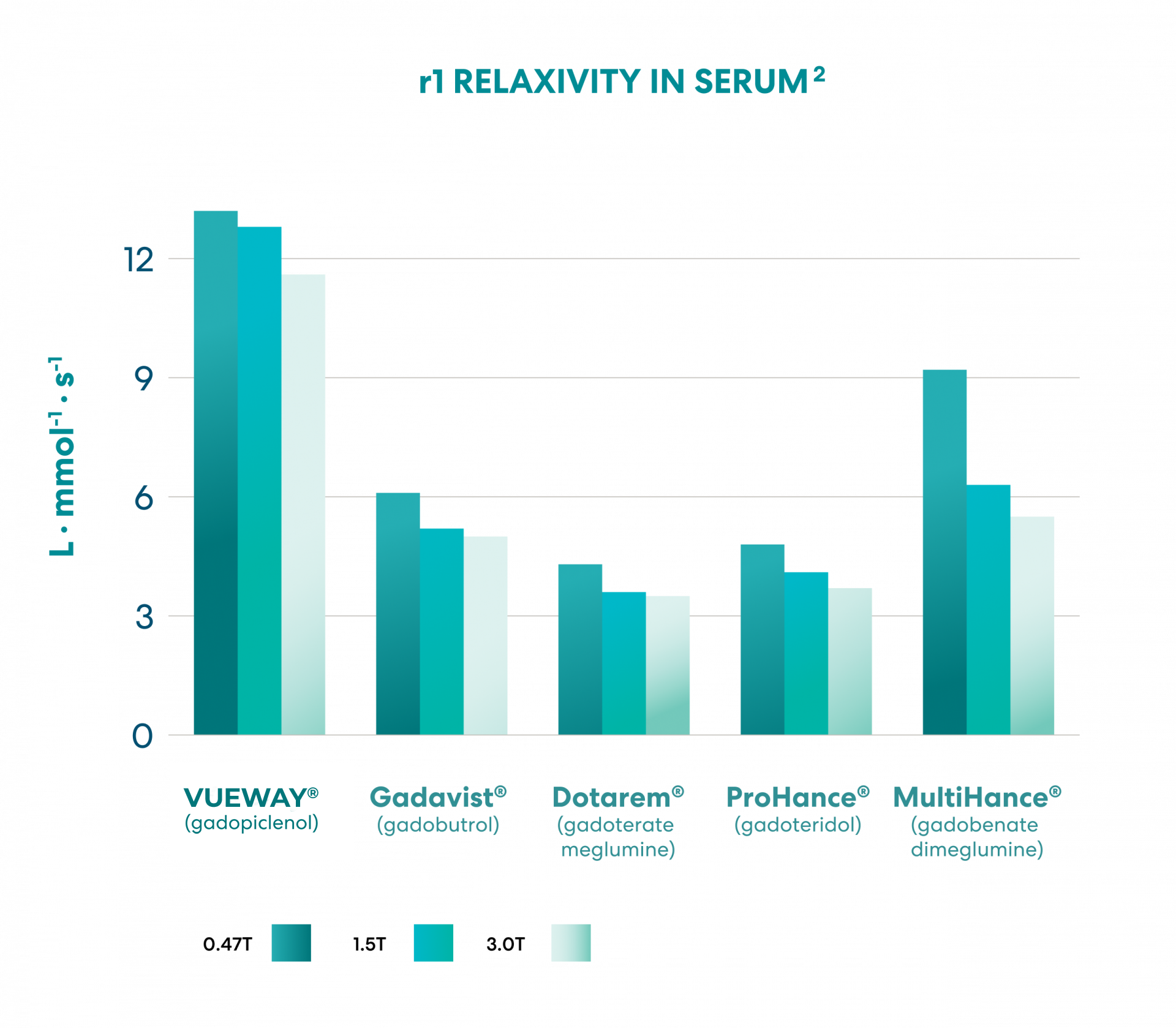
Gadopiclenol:
The highest relaxivity
of all GBCAs today2
Gadopiclenol demonstrates the highest relaxivity in water and serum vs. all currently approved linear and macrocyclic GBCAs at all field strengths.2
The degree of contrast enhancement and diagnostic efficacy produced by GBCAs on MR images depends on relaxivity.12
Explore VUEWAY®(gadopiclenol) injection for intravenous use
Effective contrast enhancement at half the gadolinium dose (0.05 mmol/kg) vs. a macrocyclic GBCA at a dose of 0.1 mmol/kg in approved indications in the U.S.1
A lower gadolinium dose for similar visualization can help address the unmet medical need to minimize Gd exposure per MRI procedure and reduce the overall lifetime dose.13,14

Charts based on Robic C et al. Invest Radiol 2019
Gadopiclenol: The most approved MRI indications to detect and visualize lesions.1
VUEWAY Injection offers efficiency with a single dosing regimen that can be adapted to multiple procedures to help simplify inventory management and workflow. 1
Central Nervous System
Brain
Spine
Associated tissues
Body
Head and neck
Thorax
Abdomen
Pelvis
Musculoskeletal system
![]()
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. VUEWAY, MultiHance, and ProHance are not approved for intrathecal use.
Dosage Forms
VUEWAY® is available in single-dose vials, single-dose prefilled syringes, pharmacy bulk packages, and imaging bulk package.
The VUEWAY Imaging Bulk Package (IBP) is for intravenous use and not for direct infusion. IBP is used for dispensing multiple single doses of gadopiclenol injection for multiple patients, using an automated contrast injection system, or contrast management system approved or cleared for use with this contrast agent in this Imaging Bulk Package. See drug and device labeling for information on devices indicated for use with this Imaging Bulk Package and techniques to help assure safe use.
Indications
VUEWAY injection is indicated in adults and children aged 2 years and older for use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to detect and visualize lesions with abnormal vascularity in:
- the central nervous system (brain, spine, and associated tissues),
- the body (head and neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and musculoskeletal system).
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- Chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m²), or
- Acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g., age > 60 years, hypertension, diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended VUEWAY dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to any re-administration.
Contraindications
VUEWAY injection is contraindicated in patients with history of hypersensitivity reactions to VUEWAY.
Warnings and Precautions
There are risks associated with intrathecal use of GBCAs that can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of VUEWAY have not been established with intrathecal use and VUEWAY is not approved for intrathecal use.
Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is increased in patients using GBCA agents that have impaired elimination of the drugs, with the highest risk in patients with chronic, severe kidney disease as well as patients with acute kidney injury. Avoid use of GBCAs among these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrast MRI or other modalities.
Hypersensitivity reactions, including serious hypersensitivity reactions, could occur during use or shortly following VUEWAY administration. Assess all patients for any history of a reaction to contrast media, bronchial asthma and/or allergic disorders, administer VUEWAY only in situations where trained personnel and therapies are promptly available for the treatment of hypersensitivity reactions, and observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions after administration.
Gadolinium retention can be for months or years in several organs after administration. The highest concentrations (nanomoles per gram of tissue) have been identified in the bone, followed by other organs (brain, skin, kidney, liver and spleen). Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies, when possible.
Acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs in patients with chronically reduced renal function. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent.
Extravasation and injection site reactions can occur with administration of VUEWAY. Ensure catheter and venous patency before the injection of VUEWAY.
VUEWAY may impair the visualization of lesions seen on non-contrast MRI. Therefore, caution should be exercised when VUEWAY MRI scans are interpreted without a companion non-contrast MRI scan.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 0.5%) are injection site pain (0.7%), and headache (0.7%).
POST-MARKETING EVENTS
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of GBCAs.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Acute pancreatitis with onset within 48 hours after GBCA administration.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information for VUEWAY (gadopiclenol) injection for intravenous use including BOXED WARNING on Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis.
Manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by BIPSO GmbH, 78224 Singen (Germany).
VUEWAY is a registered trademark of Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
MultiHance® (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL
and
ProHance® (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL
Indications and Usage for MultiHance® (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the central nervous system (CNS) in adults and pediatric patients (including term neonates) to visualize lesions with abnormal blood-brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) to evaluate adults with known or suspected renal or aorto-ilio-femoral occlusive vascular disease
Indications and Usage for ProHance® (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL:
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
ProHance is indicated for use in MRI in adults and pediatric patients including term neonates to visualize lesions with disrupted blood-brain barrier and/or abnormal vascularity in the brain (intracranial lesions), spine, and associated tissues.
EXTRACRANIAL/EXTRASPINAL TISSUES
ProHance is indicated for use in MRI in adults to visualize lesions in the head and neck.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION for MultiHance and ProHance:
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. MultiHance and ProHance are not approved for intrathecal use.
NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) increase the risk for NSF among patients with impaired elimination of the drugs. Avoid use of GBCAs in these patients unless the diagnostic information is essential and not available with non-contrasted MRI or other modalities. NSF may result in fatal or debilitating systemic fibrosis affecting the skin, muscle and internal organs.
- The risk for NSF appears highest among patients with:
- chronic, severe kidney disease (GFR < 30 mL/min/1.73m²), or
- acute kidney injury.
- Screen patients for acute kidney injury and other conditions that may reduce renal function. For patients at risk for chronically reduced renal function (e.g. age > 60 years, hypertension or diabetes), estimate the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) through laboratory testing.
- For patients at highest risk for NSF, do not exceed the recommended MultiHance and ProHance dose and allow a sufficient period of time for elimination of the drug from the body prior to re-administration.
MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL
CONTRAINDICATIONS
MultiHance is contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to gadolinium-based contrast agents.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of MultiHance have not been established with intrathecal use and MultiHance is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: NSF has occurred in patients with impaired elimination of GBCAs. Higher than recommended dosing or repeated dosing appears to increase risk.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of MultiHance administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment. Consider the risk for hypersensitivity reactions, especially in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions or a history of asthma or other allergic disorders.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen. At equivalent doses, retention varies among the linear agents. Retention is lowest and similar among the macrocyclic GBCAs. Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established, but they have been established in the skin and other organs in patients with impaired renal function. Minimize repetitive GBCA imaging studies, particularly closely spaced studies when possible.
Acute Renal Failure: In patients with renal insufficiency, acute renal failure requiring dialysis or worsening renal function have occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of renal failure may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent. Screen all patients for renal dysfunction by obtaining a history and/or laboratory tests.
Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions: Extravasation of MultiHance may lead to injection site reactions, characterized by local pain or burning sensation, swelling, blistering, and necrosis. Exercise caution to avoid local extravasation during intravenous administration of MultiHance.
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Cardiac arrhythmias have been observed in patients receiving MultiHance in clinical trials. Assess patients for underlying conditions or medications that predispose to arrhythmias. The effects on QTc by MultiHance dose, other drugs, and medical conditions were not systematically studied.
Interference with Visualization of Certain Lesions: Certain lesions seen on non-contrast images may not be seen on contrast images. Exercise caution when interpreting contrast MR images in the absence of companion non-contrast MR images.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions are nausea (1.3%) and headache (1.2%).
POST-MARKETING EVENTS
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of MultiHance, Prohance, or other GBCAs:
Acute pancreatitis within 48 hours of GBCA administration has been reported.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: Acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
Lactation: There is no information on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or the effects of the drug on milk production. However, limited literature reports that breastfeeding after MultiHance administration to the mother would result in the infant receiving an oral dose of 0.001%-0.04% of the maternal dose.
Pediatric Use: MultiHance is approved for intravenous use for MRI of the CNS to visualize lesions with abnormal blood brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues in pediatric patients from birth, including term neonates, to less than 17 years of age. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were similar to those reported in adults. No dose adjustment according to age is necessary in pediatric patients two years of age and older. For pediatric patients, less than 2 years of age, the recommended dosage range is 0.1 to 0.2 mL/kg. The safety of MultiHance has not been established in preterm neonates.
ProHance (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in patients with known allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to ProHance.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use: Intrathecal administration of GBCAs can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. The safety and effectiveness of ProHance have not been established with intrathecal use and ProHance is not approved for intrathecal use.
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: NSF has occurred in patients with impaired elimination of GBCAs. Higher than recommended dosing or repeated dosing appears to increase risk.
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions have been reported, involving cardiovascular, respiratory, and/or cutaneous manifestations. Some patients experienced circulatory collapse and died. In most cases, initial symptoms occurred within minutes of administration and resolved with prompt emergency treatment. Prior to ProHance administration, ensure the availability of trained personnel and medications to treat hypersensitivity reactions. Consider these risks, especially in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions or a history of asthma or other allergic disorders.
Gadolinium Retention: Gadolinium is retained for months or years in several organs. The highest concentrations have been identified in the bone, followed by brain, skin, kidney, liver, and spleen. Linear GBCAs cause more retention than macrocyclic GBCAs. Consequences of gadolinium retention in the brain have not been established, but they have been established in the skin and other organs in patients with impaired renal function.
Acute Kidney Injury: In patients with chronically reduced renal function, acute kidney injury requiring dialysis has occurred with the use of GBCAs. The risk of acute kidney injury may increase with increasing dose of the contrast agent; administer the lowest dose necessary for adequate imaging.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions are nausea and taste perversion with an incidence ≥ 0.9%.
POST-MARKETING EVENTS
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of MultiHance, Prohance, or other GBCAs:
Acute pancreatitis within 48 hours of GBCA administration has been reported.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Acute respiratory distress syndrome, pulmonary edema.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: GBCAs cross the human placenta and result in fetal exposure and gadolinium retention. Use only if imaging is essential during pregnancy and cannot be delayed.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. However, published lactation data on other GBCAs indicate that 0.01 to 0.04% of the maternal gadolinium dose is present in breast milk.
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of ProHance have been established for use with MRI to visualize lesions with abnormal blood brain barrier or abnormal vascularity of the brain, spine, and associated tissues in pediatric patients from birth, including term neonates, to 17 years of age. Adverse reactions in pediatric patients were similar to those reported in adults. No case of NSF associated with ProHance or any other GBCA has been identified in pediatric patients ages 6 years and younger.
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for MultiHance Multipack.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for ProHance (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL.
Please click here for full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide for additional safety information for ProHance Multipack.
MultiHance is manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by BIPSO GmbH – 78224 Singen (Germany) and by Patheon Italia S.p.A, Ferentino, Italy.
ProHance is manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by BIPSO GmbH – 78224 Singen (Germany).
MultiHance is a registered trademark of Bracco International B.V.
MultiHance Multipack is a trademark of Bracco International B.V.
ProHance is a registered trademark of Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
ProHance Multipack is a trademark of Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3™ (the Bracco-branded Max 3™, a Rapid Exchange and Syringeless MR Injector System) is distributed by Bracco Diagnostics Inc.
Indications for use
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 (XD 10180) is a contrast media management system that is indicated for the controlled, automatic administration, on the venous side, of contrast media and saline (NaCl), to human subjects undergoing diagnostic examinations in magnetic resonance (MR) applications.
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 (XD 10180) is specifically indicated for use in MRI procedures for the delivery of the following contrast media:
- Gadobutrol Injection in single-dose (SD) container or Imaging Bulk Package (IBP)
- Gadopiclenol Injection in SD container or IBP
- Gadobenate dimeglumine Injection in SD container
- Gadoterate meglumine Injection in SD container
Easy-Click-Cassette – flex Max 3 is used for a maximum time of twenty-four (24) hours or a maximum of 96 bottles of contrast media, whichever comes first.
Use time expiration per SD container is a maximum of four (4) hours, unless otherwise stated by the contrast media labeling.
Use time expiration per IBP or saline container is a maximum of twenty-four (24) hours, unless otherwise stated by the media labeling.
Spike for MRI disposable is for single-bottle use only and must be discarded with the media container. The Patient tubing must be discarded after each patient procedure.
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 (XD 10180) is to be used only by and under quasi-continuous supervision of trained healthcare professionals in an appropriate licensed healthcare facility, in a room designated for radiological procedures that involve intravascular administration of contrast agent.
The ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 (XD 10180) is not intended for injection of contrast media (CM) for high-pressure angiography.
Contraindications
The ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 injectors are not intended for the administration of contrast medium during high-pressure angiography or other applications that do not comply with the intended use.
The injector is not protected against the effects of defibrillation. Before a defibrillator is used, the patient must be disconnected from ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 injector.
Do not add any disposables (i.e. connector tubing or valves) to the ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 disposables or in conjunction with the patient tubing that are not provided by ulrich medical.
No valves or other connectors may be placed in-line between the patient tubing and the patient cannula. The disposables identified in this IFU are designed, manufactured, and tested for connection with cannulas for pressure injections.
Do not use ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 injectors with any other contrast media (other than those described in this IFU). Any other contrast media are inappropriate and should not be used.
Do not operate the injector and terminal, including any accessories, in potentially explosive atmospheres or in the vicinity of combustible materials (especially anesthetic drugs, detergents, and oxygen-enriched environments).
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 is manufactured by ulrich GmbH & Co. KG.
ulrich medical is a registered trademark of ulrich GmbH & Co. KG.
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 is a trademark of ulrich GmbH & Co. KG.
ulricheasyINJECT Max 3 is distributed as the Bracco-branded Max 3, a Rapid Exchange and Syringeless MR Injector System, by Bracco Diagnostics Inc.; 510 Carnegie Center, Suite 300, Princeton, NJ 08540 USA; Phone: (800) 631-5245; Fax: (609) 514-2424; Customer Service: 1-877-BRACCO 9 (1-877-272-2269); Scientific Information: 1-800-257-5181 (Option 2); Website: https://smartinject.com/max3/
AiMIFY™ Software
Indications for Use
AiMIFY is an image processing software that can be used for image enhancement in MRI images. It can be used to increase contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), contrast enhancement (CEP), and lesion-to-brain ratio (LBR) of enhancing tissue in brain MRI images acquired with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. It is intended to enhance MRI images acquired using standard approved dosage per the contrast agent’s instructions for use.
Cautions
AiMIFY-enhanced images should not be used alone to assist patient diagnosis. The standard post-contrast image must always be reviewed first before using AiMIFY-enhanced images for patient diagnosis.
Please be aware that AiMIFY is not intended for artifact reduction, such as metal artifact and motion artifact. Enhanced images may have similar artifacts as input images.
AiMIFY may enhance intensity differences between pre-and post-contrast images that are caused by 1) registration errors between the sequences or 2) image artifacts in either sequence.
AiMIFY may enhance vessel conspicuity more than standard acquired post-contrast images. In cases where vessel conspicuity interferes with or delays diagnosis, the standard post-contrast image should be used for adjudication.
AiMIFY-enhanced images may contain false lesions due to enhancement of image quality issues in either input sequences, due to being introduced by the AiMIFY algorithm, or both. The standard post-contrast image should be used to rule out false lesions.
Please be aware that AiMIFY has only been trained and tested on head MRI for contrast enhancement. Using the AiMIFY software in other anatomies or use cases not defined in this user manual could result in unknown image enhancement performance.
The internal morphology of tissue in input sequences have been tested to be moderately preserved by AiMIFY processing both for lesion tissue and parenchyma tissue. Internal morphology may appear to be missing due to window leveling of the image, and can be obtained by adjusting the window levels.
Please be aware that AiMIFY is intended for use only with standard of care quality images. Standard approved dose contrast images should be acquired per the contrast agent’s instructions for use. The standard of care should not be adjusted in preparation for using AiMIFY.
Please be aware that AiMIFY should not be used for acquiring stat scans or emergent scans, as image processing time may delay diagnosis.
Standard approved dose contrast images should be acquired per the contrast agent’s instructions for use. AiMIFY-enhanced images are not fully equivalent to post-contrast images acquired with a higher than recommended actual dosage of contrast. However, the high-dose-like appearance of AiMIFY-enhanced images offers a potentially safer alternative to actually acquiring post-contrast images beyond standard dosing.
Contraindications
AiMIFY is an image processing software that inherently doesn’t cause harm to patients of any subpopulation. However, gadolinium-based contrast agents are associated with contraindications, precautions, and warnings for certain subpopulations. Strictly follow the gadolinium-based contrast agent’s instructions for use, including but not limited to contraindicated patient populations, prior to processing with AiMIFY.
Limitations
AiMIFY has been trained and tested using a diverse DICOM image dataset collected from different MR imaging applications at 0.3T, 1.5T, and 3.0T, including:
- T1 weighted imaging for pre and post-contrast brain scans obtained with gadolinium-based contrast agents in 2D sequences, such as fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and fast spin echo (FSE).
- T1 weighted imaging for pre and post-contrast brain scans obtained with gadolinium-based contrast agents in 3D sequences, such as BRAin VOlume (BRAVO) inversion-recovery-prep fast split echo (SPGR) and Magnetization Prepared Rapid Gradient Echo (MPRAGE).
- Acquisition in axial, coronal, and sagittal orientations.
- Images acquired with GE Medical Systems, Philips Medical Systems, Siemens Healthineers, and Hitachi scanners (see separate Scanner List for models).
- Images (for performance testing) spanning a variety of pathologies including patients with Cerebritis, Glioma, Inflammation, Lymphoma, Meningioma, Metastatic lesions, Multiple sclerosis, Neuritis, other tumor-related lesions (e.g., resection/radiation necrosis / suspected cyst / etc.), and other abnormalities.
- Patients aged 7 to 86 years old with an even distribution of females and males in the test dataset.
- Lesions in the dataset were small (<1 cc) and large (>1 cc).
Any imaging sequences/applications outside the above list may result in prolonged processing time and/or unreasonable results.
AiMIFY is manufactured for Bracco Diagnostics Inc. by Subtle Medical Inc. – Menlo Park, CA, USA 94025.
AiMIFY is a trademark of Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION | INDICATIONS AND USAGE
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: RISK ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL USE and NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS
Risk Associated with Intrathecal Use
Intrathecal administration of gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) can cause serious adverse reactions including death, coma, encephalopathy, and seizures. VUEWAY, MultiHance, and ProHance are not approved for intrathecal use.
References:
1. VUEWAY® (gadopiclenol) injection for intravenous use Full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide. Princeton, NJ: Bracco Diagnostics Inc.; December 2025.
2. Robic C, Port M, Rousseaux O, et al. Physicochemical and Pharmacokinetic Profiles of Gadopiclenol: A New Macrocyclic Gadolinium Chelate With High T1 Relaxivity. Invest Radiol. 2019 Aug;54: 475-484.
3. Spinazzi A, Lancelot E, Vitali L, et al. Safety of gadopiclenol after its first year of clinical use. Invest Radiol. ():10.1097/RLI.0000000000001144, November 21, 2024. | DOI: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001144
4. Loevner LA, Kolumban B, Hutóczki G, et al. Efficacy and safety of gadopiclenol for contrast-enhanced MRI of the central nervous system: the PICTURE randomized clinical trial. Invest Radiol. 2023 May;58(5):307-313.
5. Kuhl C, Csőszi T, Piskorski W, Miszalski T, Lee JM, Otto PM. Efficacy and Safety of Half-Dose Gadopiclenol versus Full-Dose Gadobutrol for Contrast-enhanced Body MRI. Radiology. 2023 Jul; 308(1): e222612.
6. MultiHance® (gadobenate dimeglumine) injection, 529 mg/mL Full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide. Princeton, NJ: Bracco Diagnostics Inc.; March 2025.
7. Seidl Z, Vymazal J, Mechl M, et al. Does higher gadolinium concentration play a role in the morphologic assessment of brain tumors? Results of a multicenter intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobutrol versus gadobenate dimeglumine (the MERIT Study). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012 Jun-Jul;33(6):1050–1058.
8. Vaneckova M, Herman M, Smith MP, et al. The benefits of high relaxivity for brain tumor imaging: results of a multicenter intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine with gadoterate meglumine (The BENEFIT Study). AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2015 Sep;36(9):1589–1598..
9. Maravilla KR, Maldjian JA, Schmalfuss IM, et al. Contrast enhancement of central nervous system lesions: multicenter intraindividual crossover comparative study of two MR contrast agents. Radiology. 2006 Aug;240(2):389–400.
10. Rowley HA, Scialfa G, Gao PY, et al. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of brain lesions: a large-scale intraindividual crossover comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine versus gadodiamide. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Jul;29(9):1684–1691.
11. ProHance® (Gadoteridol) Injection, 279.3 mg/mL Full Prescribing Information and Patient Medication Guide. Princeton, NJ: Bracco Diagnostics Inc.; March 2025.
12. Tweedle MF, Kanal E and Muller R. Considerations in the Selection of a New Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent. Applied Radiology. Supplement May 2014.
13. Runge VM and Heverhagen, JT. Advocating the Development of Next-Generation High-Relaxivity Gadolinium Chelates for Clinical Magnetic Resonance. Invest Radiol. 2018 Jul;53(7):381-389.
14. Lancelot E, Raynaud JS, Desché P. Current and Future MR Contrast Agents: Seeking a Better Chemical Stability and Relaxivity for Optimal Safety and Efficacy. Invest Radiol. 2020 Sep;55(9):578-588.
15. Data on file, Bracco Diagnostics Inc.: January 2025.